In music, the term “texture” refers to the way different musical elements, such as melodies, harmonies, and rhythms, are combined and layered to create the overall sound and feel of a piece of music. Texture describes the relationship between the different musical parts and how they interact with each other. It can vary greatly and greatly affect the character and mood of a piece of music.
There are several types of musical texture commonly discussed in music theory:
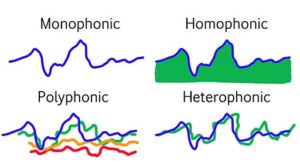
- Monophonic texture: This refers to a single melodic line without any accompanying harmonies or additional voices. It is the simplest form of texture and is often used in unaccompanied solo performances or chants.
- Homophonic texture: This refers to a musical texture where there is one dominant melodic line accompanied by harmonies that support or accompany the melody. This is the most common type of texture in Western music and is often used in songs, hymns, and many popular music genres.
- Polyphonic texture: This refers to a musical texture where multiple melodic lines are played simultaneously, creating independent and interwoven melodies. Each voice has its own melodic and rhythmic characteristics, and they can interact with each other in complex ways. Examples of polyphonic music include fugues and canons.
- Heterophonic texture: This refers to a texture where multiple performers are playing or singing a slightly different version of the same melody at the same time, resulting in slight variations or ornamentations. This texture is often found in folk music traditions and improvisatory styles.
- Thick vs. thin texture: Texture can also be described as thick or thin, depending on the number of musical elements and voices present. A thick texture refers to a dense and complex arrangement with many musical parts, while a thin texture refers to a sparse arrangement with fewer musical parts.
Texture is an important aspect of music that contributes to its overall richness, complexity, and emotional impact. Musicians and composers carefully consider and manipulate texture to create the desired musical effect in a piece of music.